Introduction
Movement can be initiated from a variety of positions. To attain a position we start at one and end in another. Posture is a position which one holds their body when standing, sitting or position it in a way appropriate to the movement that is desirable kneeling, lying or for a specific work.
The postures from which the movement is initiated are known as starting positions, these can either be active or passive in nature.There are 5 fundamental starting positions[1]
- Standing
- Kneeling
- Sitting
- Lying
- Hanging
All other positions are derived from these positions by altering the positions of arms, trunk and legs and are known to be Derived Positions. All exercises begin in one of the starting positions and altered by moving into another position or modified according to the need. A balance of forces acting on the body maintain equilibrium and stability in these positions. Postural reflexes control strength and distribution of contractions.
Standing
In standing the whole body must be balanced and stabilized in correct alignment on feet with a small base of support by coordinated work of many muscle groups.It is the Most difficult of positions, the position is described as below[1]
| Heels | Together, in same line, toes slightly apart |
|---|---|
| Knees | Together & straight |
| Hips | Extended & slightly laterally rotated |
| Pelvis | Balanced on femoral heads |
| Spine | Stretched to maximum length |
| Head | Thrust upwards, ears leveled & eyes look straight forward |
| Shoulders | Down & back |
| Arms | Hang loosely to sides |
| Palm | Facing inwards towards body |
Muscle work
When the Body segments are in good alignment and perfectly balanced the muscle work is minimum. This increases as movement occurs or the forces keeping the alignment disturbs.
Muscles |
Work |
|---|---|
| Intrinsic muscles of feet | Stabilizes feet & Prevents toe curling |
| Plantar flexors | Balances lower leg on foot |
| Dorsiflexors | Counterbalances plantarflexors & support
medial longitudinal arch of foot |
| Evertors | Counterbalances action of invertors
Presses ball of Great toe on ground |
| Knee extensors | works slightly |
| Hip extensors | Maintains hip extension
Balances pelvis on femoral heads |
| Hip Lateral rotators(Slight action) | Bracing of legs & foot arches |
| Spinal extensors | Keeps trunk straight |
| Lumbar flexors | Prevents over action of lumbar extensors
Maintain correct angle of pelvic tilt Supports abdomonal viscera |
| Pre vertebral neck muscles | Controls extensive neck extension
Straightens cervical spine |
| Flexors/extensors of atlanto-occipital joint | Work reciprocally to balance head |
| Elevators of mandible | Closes the mouth |
| Scapular retractors | draws the scapulae back wards |
| Arms | Relaxed |
Effects and Uses
Due to small base of support this position is less stable, high COG. This position is suitable to persons who can perfectly balance and maintain it correctly.
This is suitable for performing many exercises, if maintain correctly reduces muscle work and conditions the postural reflex.[1]
Kneeling
In this position the body is supported on the knees which can be together or slightly apart. The feet are plantar flexed if kneeling on ground or in in mid position if on plinth, this is often used in praying
Muscle work
The lower leg is relaxed and the body is supported on the knees[1]
| Muscle | Work |
|---|---|
| Flexors & extensors of knee | Inter play to balance femora vertically on the knees |
| Extensors of Hip and flexors of lumbar spine | Maintain correct angle of pelvic tilt |
Remaining work of the muscles is alike that of in standing
Effects and uses
This position is slightly stable than standing because of increase in the base of support but is the most uncomfortable of positions
Sitting
This position is taken in chair or stool and the hips and knees are flexed to right angle and the feet rest on the floor[1] Most used position in daily life
Muscle work
This position does not need much of work to be done by the legs to hold on to the position, the flexors of hips work to maintain a right angle and prevent the tendency to slump
Effects and Uses
This is the most comfortable of positions and is very stable, rotation is limited to spine as the pelvis bears the weight of the upper body and is fixed, suitable for non weight bearing exercises of the knee and foot can be performed in this position and also suitable for training correct alignment of upper body in habitual sitting.
Lying
Lying is the most easiest of the fundamental positions and most of us spend few hours as in sleeping or relaxing and most preferred position for rest
it is as stable as possible
Muscle work
Muscle work in lying is minimal not much movement occurs in this position is taken on a soft mattress as it gives way to the contours of the body but if taken on a plinth or a hard surface the head can roll to either sides[1]
| Muscle | Work |
|---|---|
| Head rotators | work reciprocally to stabilize the position |
| Extensors of hip & flexors of lumbar spine | work to hollow the back |
| Medial rotators of hip | keeps legs in neutral position |
Effects and Uses
The spine is relieved of weight of the upper body suitable for many exercises and in the treatment of spinal deformities, unsuitable for patients with respiratory or heart conditions due to increased pressure of abdominal viscera and elderly due the hindrance to return of blood from heart
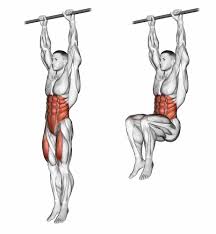
Hanging
In hanging body is suspended by grasping onto something with the fingers and palm
Muscle work
| Muscle | Work |
|---|---|
| Flerors of fingers | grasping |
| Wrist | reduce stain on joints & synnergists to finger flexors |
| Flexors of elbow | reduce stain on joints |
| Adductors of shoulder | Lift the body on arms |
| Depressors, retractors & medial rotators | fix scapulae and brace upper back |
| Pre vertebral post neck | Maintain the position of head and neck |
| Flexors of lumbar spine | Correct the tendency to arch the back |
| Adductors of hips | Keep legs together |
| Extensors of knees | Maintain full extension |
| Plantar flexors | Point toes to floor |
Effects and Uses
Hanging requires extensive work of upper back and arms so people with strong muscles to maintain the body weight can use this position[1]. Children enjoy this position in play not suitable for weak individuals
References