Objective
The Foot and Ankle Disability Index (FADI)[1][2][3][4] is a region-specific self-report of function, firstly described in 1999 by Martin et al.
The FADI is a former version of the FAAM. The 2 instruments are identical except for an additional 5 items found on the FADI. Four of these items assess pain, and the fifth item evaluates an individual’s ability to sleep. These 5 items were subsequently removed from the ADL subscale to improve psychometric properties of the instrument. The sports subscale remained unchanged, resulting in a new instrument, the FAAM.
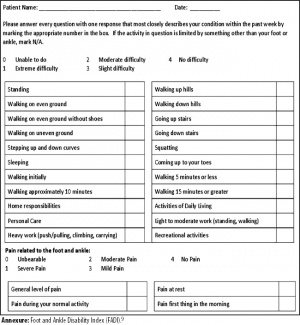
The Foot and Ankle Disability Index is a 34-item questionnaire divided into two subscales: the Foot and Ankle Disability Index and the Foot and Ankle Disability Index Sport. The FADI has 26 items, and the FADI Sport has 8. The FADI contains 4 pain related items and 22 activity related items. The FADI Sport contains 8 activity related items. It assesses more difficult tasks that are essential to sport. The FADI Sport is unique in that it is a population-specific subscale designed for athletes. It is designed to address this need by detecting deficits in higher functioning subjects.
Intended Population
The foot and ankle disability index was designed to assess functional limitations related to foot and ankle conditions. Hale and Hertel [1] advocate the use of the FADI and FADI Sport self-report instruments in clinical care and research applications in young adults with CAI.
Eechaute et al [2] concluded that the FADI and FAAM were the most appropriate evaluative instruments to quantify functional disabilities in athletes with chronic ankle instability. An advantage of the FADI and FAAM is that they both have a sports subscale in addition to an activities of daily living subscale. The sports subscale may be particularly useful when addressing the limitations of athletes with CAI.
Method of Use
Each of the 34 items is scored on a 5-point Likert scale from 0 (unable to do) to 4 (no difficulty at all). The 4 pain items of the FADI are scored 0 (none) to 4 (unbearable). The FADI has a total point value of 104 points, whereas the FADI Sport has a total point value of 32 points. The FADI and FADI Sport are scored separately as percentages, with 100% representing no dysfunction.[1][2][3]
Evidence
Hale and Hertel [1] examined the reliability and sensitivity of both FADI and FADI Sport and reported that both scales are:
- reliable in detecting functional limitations in subjects with CAI
- sensitive to differences between healthy subjects and subjects with CAI
- responsive to improvements in function after rehabilitation in subjects with CAI.
Reliability
Using Bivariate correlations Hale & Hertel reported a significant relationship between the FADI and the FADI Sport. The correlation for the two scales for the involved ankles was (0.64). contrary to (0.84) which resulted from a combined analysis of the uninvolved extremities of CAI subjects with the matched extremities of healthy subjects.The correlation between the baseline FADI and FADI Sport scores was statistically significant (P <.0005 among healthy subjects and with cai. id="cite_ref-p1_1-4" class="reference">[1]
Validity
Construct validity of FADI and FADI sport: Significantly lower scores on the involved versus uninvolved side (p[4]
Validity of FADI and FADI sport was also assessed by Pugia et al through investigating the correlations among both scales , ankle girth measures, weight-bearing status, and the Ankle Osteoarthritis Scale after acute ankle sprains. Moderate to good correlations were noted among the functional measures and between the functional measures and weight-bearing status.[6]
Responsiveness
Subjects scored significantly higher on the FADI and FADI sport after 4 weeks of rehabilitation (p[2]
FADI: Significant difference after 6 weeks of training: pre training score =87.1% (± 12,1) post training score = 94.4% (± 6,1) ES = 0.52 (n =16)
FADI Sport: Significant difference after 6 weeks of training: pre training score = 78.4% (± 12,9)post training score = 89.5% (± 11,3) ES = 0.71 (n = 16)
References
- ↑ 1.01.11.21.31.4 Sheri A. Hale and Jay Hertel†. Reliability and Sensitivity of the Foot and Ankle Disability Index in Subjects With Chronic Ankle Instability. Journal of Athletic Training 2005;40(1):35–40.
- ↑ 2.02.12.22.3 Eechaute et al. The clinimetric qualities of patient-assessed instruments for measuring chronic ankle instability: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2007, 8:6 doi:10.1186/1471-2474-8-6.
- ↑ 3.03.1 Christopher R. Carcia et al. Validity of the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure in Athletes With Chronic Ankle Instability. Journal of Athletic Training 2008;43(2):179–183.
- ↑ 4.04.1 Robroy L. Martin. A survey of self-reported outcome instruments for the foot and ankle. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2007;37(2):72-84. doi:10.2519/jospt.2007.2403.
- ↑ Gilani, S. F., & Amin, M. S. (2014). Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum : Is it worthwhile ? S-162, 64(12), 161–166.
- ↑ Pugia ML, Middel CJ, Seward SW. Comparison of acute swelling and function in subjects with lateral ankle injury. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2001;31:384–388.