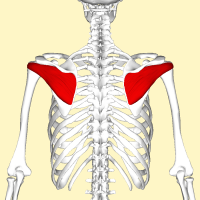
Description
A thick, triangular muscle; one of the 4 muscles which comprise the Rotator Cuff of the shoulder.
Origin
The infraspinatus fossa of scapula, with some fibres arising from the infraspinatous fascia which covers the muscle and separates it from Teres Major and Teres Minor.[1]
Insertion
The posterior aspect of greater tuberosity of humerus, and the capsule of shoulder joint.[2]
Nerve Supply
Suprascapular Nerve (C5 & C6)[3]
Blood Supply
Suprascapular and circumflex scapular arteries.[3]
Action
Infraspinatus is the main external rotator of the shoulder joint.
It assists in producing shoulder extension.
With the arm fixed, it abducts the inferior angle of the scapula. [2]
Function
It provides the primary muscle force for external rotation of the shoulder.
Along with the rest of the Rotator Cuff muscles it provides stability to the shoulder complex.[3]
Resources
References
- ↑ Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918. Available from ↑ 2.02.1 Wheeles CR. Infraspinatus. Available from: ↑ 3.03.13.2 AnatomyExpert. 3D Infraspinatus- infraspinatus. Available from: function gtElInit() { var lib = new google.translate.TranslateService(); lib.setCheckVisibility(false); lib.translatePage('en', 'pt', function (progress, done, error) { if (progress == 100 || done || error) { document.getElementById("gt-dt-spinner").style.display = "none"; } }); }