Description
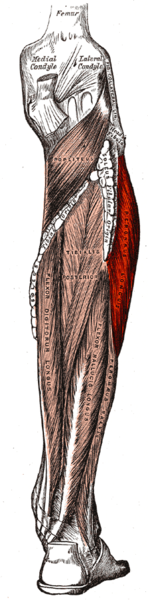
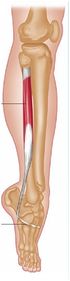
The Peroneal Longus (also known as Fibularis Longus) lies superficially at the lateral part of the lower leg. It is one of the three peroneal muscles.
Anatomy[2]
Origin
Lateral condyle of tibia,
Head and proximal two-thirds of the lateral surface of fibula,
Intermuscular septa, and
Adjacent deep fascia.
Insertion
Lateral side of base of first metatarsal and of medial cuneiform bone.
Nerve
Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve, L4,5,S1.
Artery
Fibular (peroneal) artery.
Function
Everts the foot, assists in plantar flexion and
In weight-bearing position depresses head of first metatarsal due to the strong pull on its insertion.
Maintains the transverse arch of the foot, due to how it crosses the sole of the foot.
Steadies the leg on the foot by drawing on the lateral leg, and stops it from collapsing medially.
Clinical relevance
Assessment
Peroneus longus and brevis tests
Weakness
The weakness of Peroneus lessens the ability to rise on the toes, decreases the lateral stability of the ankle and allows a varus position of the foot.
Length
Contracture results into an everted or valgus foot.
Treatment
References
- ↑ nabil ebraheim. Anatomy Of The Peroneus Longus Muscle – Everything You Need To Know – Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: ↑ Kendall, McCreary, Provance; Muscle Testing and Function; Philadelphia; 4th Edition; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1993; Peroneus Longus and Brevis; Page No:203.
- ↑ ReBalance Physiotherapy. Day -69: Peroneal Strengthening. Available from: ↑ Tim Trevail. Dry Needling: Peroneus Longus & Brevis. Available from: function gtElInit() { var lib = new google.translate.TranslateService(); lib.setCheckVisibility(false); lib.translatePage('en', 'pt', function (progress, done, error) { if (progress == 100 || done || error) { document.getElementById("gt-dt-spinner").style.display = "none"; } }); }
Ola!
Como podemos ajudar?