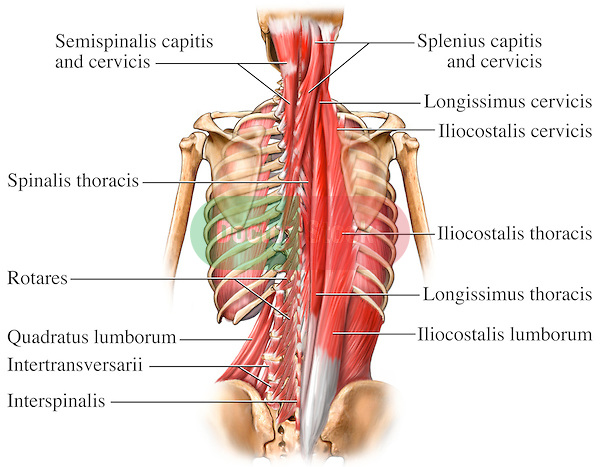
Description
Semispinalis Cervicis belongs to the Transversospinal group of muscles, formed of muscles between a spinous process and the transverse process of the vertebrae below .[1][2]
Origin
Transverse processes of T1 to T6, articular processes of the 4th to 7th cervical vertebrae[3][4]
Insertion
Spinous processes of C2 to C5[3]
Nerve Supply
Dorsal rami of cervical spinal nerves[3][4]
Blood Supply
Deep cervical artery[4]
Action
Acting bilaterally: extension of the cervical spine
Acting unilaterally: lateral flexion of the neck and rotation to the opposite side.[3]
Function
Maintains head posture.[5]
It was found that during neck pain the deep cervical extensor muscle semispinalis cervicis has shown reduction in activation [6]
manual resistance done in extension over the vertebral arch of C1 and C4 emphasized the activation of the semispinalis cervicis muscle relative to the splenius capitis at the spinal level directly caudal to the site of resistance. [6]
References
- ↑ Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/107/.
- ↑ National Center for Biotechnology Information,
Anatomy, Back, Muscles StatPearls [Internet].
available from: ↑ 3.03.13.23.3 Wheeless`textbook of orthopedic, Semispinalis Cervicis, available from:↑ 4.04.14.2 ↑ ptcentral.com/muscles/muscletrunk.html
- ↑ 6.06.1 J Schomacher, J Erlenwein, A Dieterich, F Petzke, F Petzkeb, D Falla. Can neck exercises enhance the activation of the semispinalis cervicis relative to the splenius capitis at specific spinal levels? Manual therapy, October 2015:20: 694-702.